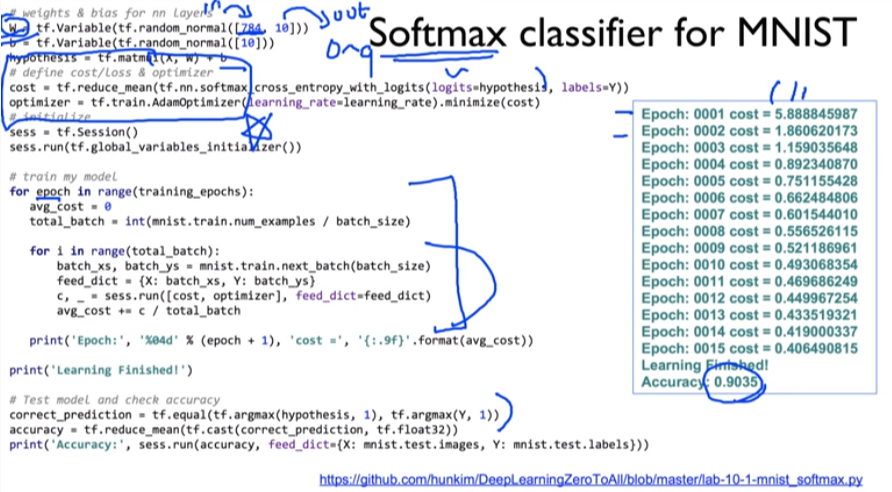
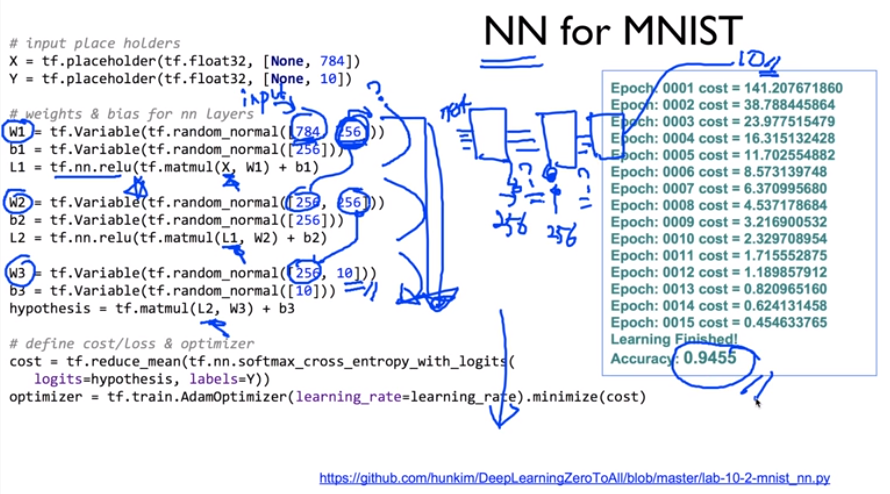
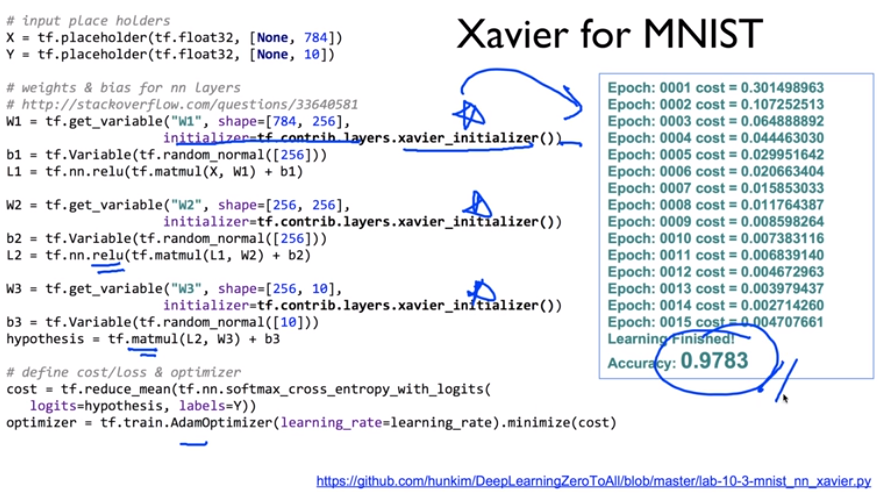
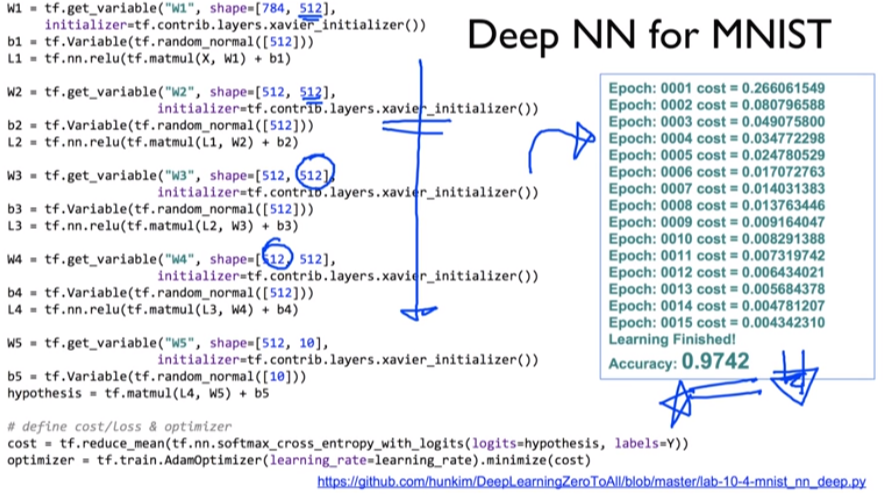
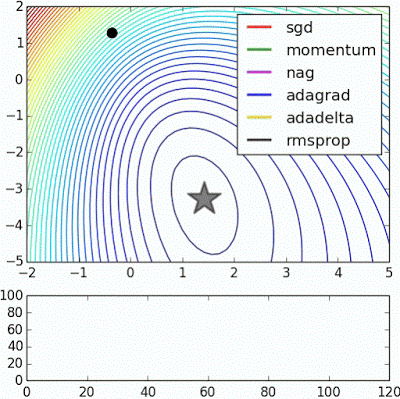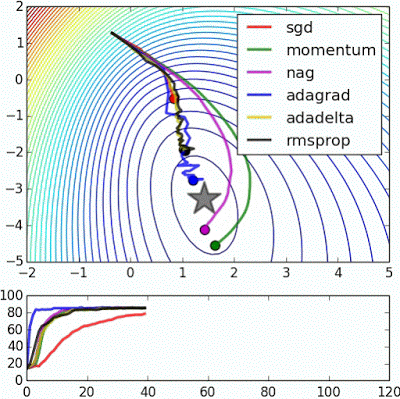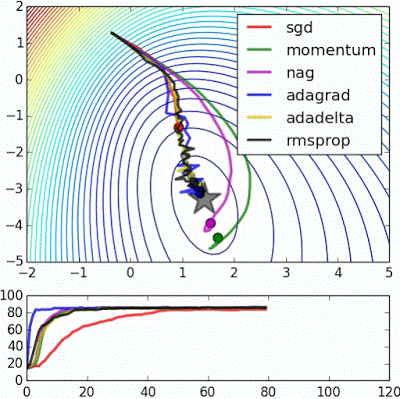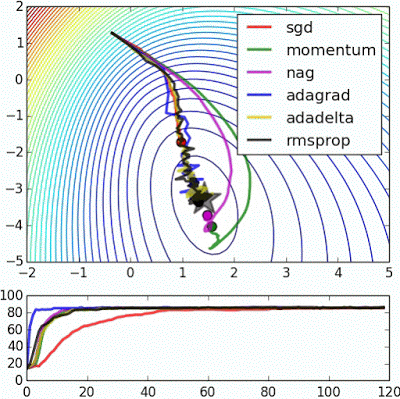
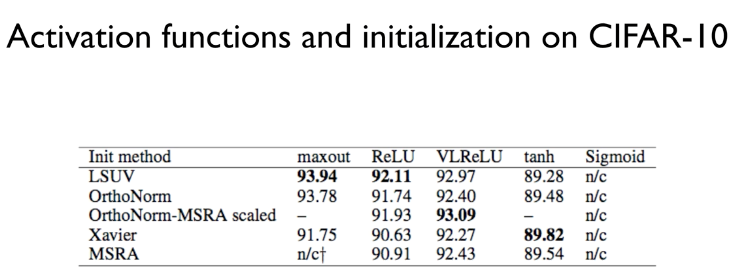
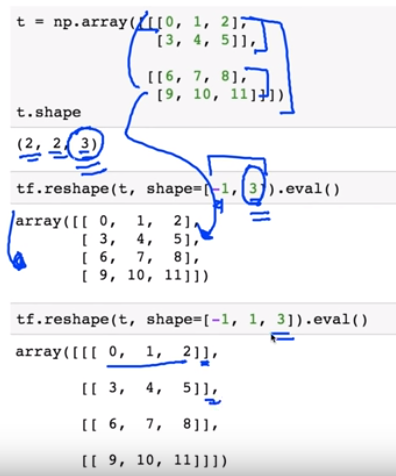
※ 김성훈 교수님의 [모두를 위한 딥러닝] 강의 정리
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?reload=9&v=BS6O0zOGX4E&feature=youtu.be&list=PLlMkM4tgfjnLSOjrEJN31gZATbcj_MpUm&fbclid=IwAR07UnOxQEOxSKkH6bQ8PzYj2vDop_J0Pbzkg3IVQeQ_zTKcXdNOwaSf_k0
- 참고자료 : Andrew Ng's ML class
1) https://class.coursera.org/ml-003/lecture
2) http://holehouse.org/mlclass/ (note)
1. XOR 알고리즘을 딥러닝으로 풀기 (원리)
- 논리적으로 매우 간단하지만 초창기 Neural Network에 큰 난관이 됨
- 하나의 Neural Network unit으로는 XOR 문제를 풀 수 없음 (수학적 증명)
- 그러나, 여러개의 Neural Network unit으로 XOR 문제 해결이 가능함
- 위의 unit을 하나로 합쳐서 표시하면, 다음과 같음
- 여러개의 logistic regression을 하나의 multinomial classification으로 변환 (행렬 이용)
- 복잡한 네트워크의 weight, bias는 학습이 불가능한 문제가 있었으나, backpropagation으로 해결 가능함
- 여러 개의 노드들이 있어 복잡한 경우에도 동일함
2. Sigmoid (시그모이드)
- Logistic regression 또는 Neural network의 Binary classification 마지막 레이어의 활성함수로 사용
- 시그모이드 함수의 그래프
- 시그모이드 함수의 미분 (뒤에서부터 순서대로 미분해 나가면 됨)
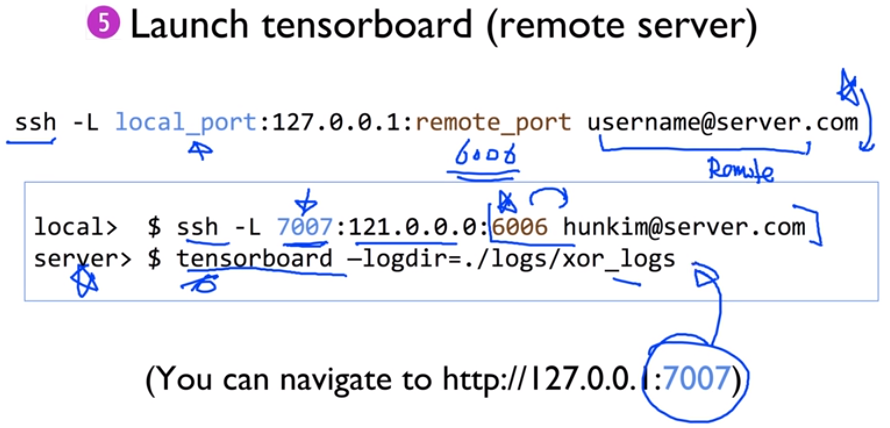
- Back propagation 미분을 위한 'TensorFlow'에서의 구현 방식 확인 (TensorBoard에서 확인 가능)
3. XOR 알고리즘을 딥러닝으로 풀기 (TensorFlow 구현)
(1) XOR 문제를 logistic regression으로 풀기
- 전체 소스코드
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
tf.set_random_seed(777 ) # for reproducibility
x_data = np.array([[0 , 0 ], [0 , 1 ], [1 , 0 ], [1 , 1 ]], dtype = np.float32)
y_data = np.array([[0 ], [1 ], [1 ], [0 ]], dtype = np.float32)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None , 2 ])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None , 1 ])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2 , 1 ]), name = " weight"
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1 ]), name = " bias"
# Hypothesis using sigmoid: tf.div(1., 1. + tf.exp(tf.matmul(X, W)))
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W) + b)
# cost/loss function
cost = - tf.reduce_mean(Y * tf.log(hypothesis) + (1 - Y) * tf.log(1 - hypothesis))
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate = 0.1 ).minimize(cost)
# Accuracy computation
# True if hypothesis>0.5 else False
predicted = tf.cast(hypothesis > 0.5 , dtype = tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, Y), dtype = tf.float32))
# Launch graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Initialize TensorFlow variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range (10001 ):
_, cost_val, w_val = sess.run(
[train, cost, W], feed_dict = {X: x_data, Y: y_data}
)
if step % 100 == 0 :
print (step, cost_val, w_val)
# Accuracy report
h, c, a = sess.run(
[hypothesis, predicted, accuracy], feed_dict = {X: x_data, Y: y_data}
)
print (" \n Hypothesis: " " \n Correct: " " \n Accuracy: "
- 결과값
Hypothesis: [[ 0.5]
[ 0.5]
[ 0.5]
[ 0.5]]
Correct: [[ 0.]
[ 0.]
[ 0.]
[ 0.]]
Accuracy: 0.5
(2) XOR 문제를 Neural Net으로 풀기
- 기존의 소스코드와 동일하나 L1, W2, b2 부분 유의
- 상기 부분만 수정하였음에도 정확도가 100%로 향상됨
- 전체 소스코드
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
tf.set_random_seed(777 ) # for reproducibility
x_data = np.array([[0 , 0 ], [0 , 1 ], [1 , 0 ], [1 , 1 ]], dtype = np.float32)
y_data = np.array([[0 ], [1 ], [1 ], [0 ]], dtype = np.float32)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None , 2 ])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None , 1 ])
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2 , 2 ]), name = ' weight1'
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2 ]), name = ' bias1'
layer1 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2 , 1 ]), name = ' weight2'
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1 ]), name = ' bias2'
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer1, W2) + b2)
# cost/loss function
cost = - tf.reduce_mean(Y * tf.log(hypothesis) + (1 - Y) * tf.log(1 - hypothesis))
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate = 0.1 ).minimize(cost)
# Accuracy computation
# True if hypothesis>0.5 else False
predicted = tf.cast(hypothesis > 0.5 , dtype = tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, Y), dtype = tf.float32))
# Launch graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Initialize TensorFlow variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range (10001 ):
_, cost_val = sess.run([train, cost], feed_dict = {X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if step % 100 == 0 :
print (step, cost_val)
# Accuracy report
h, p, a = sess.run(
[hypothesis, predicted, accuracy], feed_dict = {X: x_data, Y: y_data}
)
print (f " \n Hypothesis: \n { h} \n Predicted: \n { p} \n Accuracy: \n { a} " )
- 결과값
Hypothesis:
[[0.01338216]
[0.98166394]
[0.98809403]
[0.01135799]]
Predicted:
[[0.]
[1.]
[1.]
[0.]]
Accuracy:
1.0
'''
(3) XOR 문제를 Wide Neural Net으로 풀기
- Layer의 입력값이 많아지도록 하여, 이미지의 출력값을 증가시킴 -> Hypothesis가 향상됨 (Cost가 줄어듬)
- Wide하거나 Deep하게 학습을 시키는 경우 Cost 값이 대부분 작아짐
- 그러나 너무 잘 맞게 학습되는 경우, Overfitting 현상이 발생 가능함
(4) XOR 문제를 Deep Neural Net으로 풀기
- NN과 동일한 방법으로 단계를 여러번 반복함